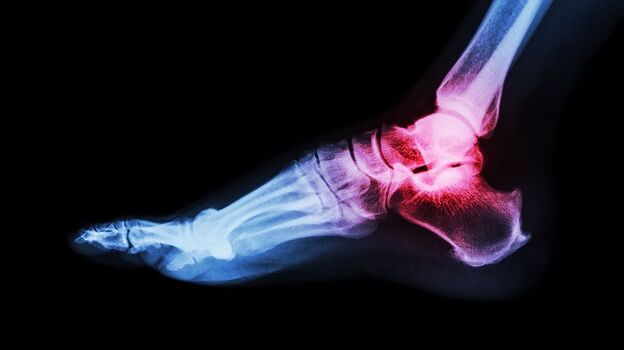
The ankle joint is often injured due to the great load to which it is subjected. A diagnosis such as osteoarthritis of the ankle is not uncommon. It is placed regardless of the age and sex of the patient. What is ankle osteoarthritis and how can it be treated?
What it is?
There is a tremendous load on the ankle. Its function is to keep the body upright. Thanks to him, a person walks and runs. With a violation of the ankle system, it is extremely difficult to lead a family way of life. What interrupts the work of the ankle?
Ankle osteoarthritis, what is it? This is a chronic disease of the joints, characterized by a degenerative course. In the cartilage of the joint irreversible processes are triggered that lead to formidable complications.
Ankle osteoarthritis develops gradually. Healthy joint surfaces are elastic and smooth. They provide cushioning under heavy loads and a smooth glide while riding. With pathology, trophism and metabolism of tissues is disturbed. The joint surface becomes inelastic and rough. During movement, cartilage comes into contact with each other, causing inflammation. When lifting weights, the main load falls on the bone, which threatens degenerative disorders.
Lack of treatment leads to more serious disorders. In 3-4 stages, cartilage and tissue damage is observed. The synovium becomes inflamed. The joint becomes unstable. Support function is violated. All these violations together lead to the fact that the movement becomes impossible.
Osteoarthritis (osteoarthritis) is one of the most common joint diseases that affects quite a large number of people.
Causes and risk factors
What is osteoarthritis of the ankle joint, we have solved it. Now let's find out what its root cause is. Ankle osteoarthritis is considered a pathology of old age. This is due to age-related body changes. Cartilage becomes thinner, bones become unstable and brittle. However, during the last decade, the diagnosis of ankle osteoarthritis has become much younger. These statistics are disappointing, as many patients ignore the early signs of the disease. Late diagnosis always threatens the development of serious complications.
Triggering factors include:
- dislocations;
- bruises
- inflammatory diseases;
- injury;
- overweight;
- altered metabolism;
- excruciating physical activity;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- autoimmune and endocrine diseases;
- osteochondrosis.

Clinical symptoms
Ankle osteoarthritis is recognized by the following characteristics:
- Pain. It is mild at first and appears after walking or exerting yourself. Sometimes when a person is in an awkward position. With the progression of the pathological process, the pain syndrome intensifies and worries already at rest.
- Swelling and inflammationThese signs appear in the context of injuries and dislocations. The body temperature in the affected area rises.
- Click. When the ankle is affected, the click is "dry" and causes an attack of pain.
- Dislocation or subluxation. Due to the thinning and degradation of the cartilage tissue, the joint becomes unstable. Bones can move and fall out of the joint capsule. These changes cause episodes of acute pain.
- Joint stiffnessWhen cartilage tissue is replaced, the bone joint stops working normally, negatively affecting its mobility.
- Joint deformityThe symptom appears in 3-4 stages of osteoarthritis. Osteophytes also lead to curvature of the ankle.
If one of the symptoms appears, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately. Treatment started on time is a step towards recovery.
Osteoarthritis of the foot and ankle joints is characterized by slow progression with a gradual development of clinical manifestations over several years.
Classification and stages
The disease develops in different ways. In some patients, several years pass from the first signs to the final stage, in others, the rapid development of the disease is observed. The speed depends on the age and state of health of the patient, the time of initiation of therapy. The symptoms of osteoarthritis of the ankle joint become brighter with the progression of the disease.
There are four stages of osteoarthritis:
- The first stage often goes unnoticed. Sometimes morning stiffness and ankle pain appear after strenuous exertion. When the foot moves, a characteristic crunch is heard. The pathological changes are not yet visible on X-rays, but the destructive process of the cartilage has already begun.
- The morning stiffness is prolonged. It takes 20 to 30 minutes to develop a leg. Lameness sometimes occurs. Osteoarthritis of the second degree of the ankle joint is recognized on x-ray by the growth of bone tissue and displacement of the bones.
- Symptoms in 3 stages are pronounced. Pain no longer only worries after heavy load, but also at rest. It is difficult for a patient to do without painkillers. Lameness increases. Crutches may be needed. The affected joint is swollen and deformed. The ankle muscles atrophy. X-ray shows a narrowing of the joint space, the formation of osteophytes, subluxation.
- Stage 4 is the most difficult. It develops as a result of lack of treatment. The cartilage is destroyed, the surfaces of the joints are fused. It is no longer possible to walk.
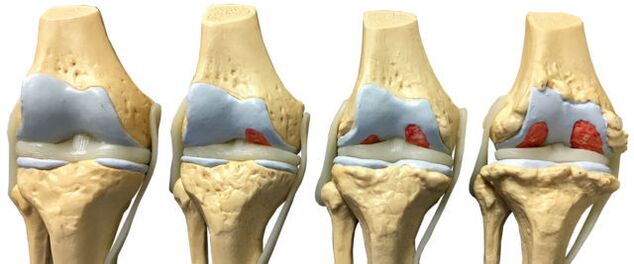
With the development of ankle osteoarthritis, there is a gradual change in the cartilage and bone tissue of the joint surfaces.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of ankle osteoarthritis is based on clinical symptoms and information obtained during examinations. Laboratory studies are considered ineffective, since there are no special tests that can detect pathology. During the remission period, all indicators are within normal limits, with an exacerbation of the disease, a clinical blood test will show a high level of C-reactive protein and ESR. These indicators indicate that the pathological process has already begun.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental methods are used:
- bone scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- Ultrasound;
- Bone scintigraphy;
- Diagnostic puncture of the joint.
Plain radiography
Plain radiography is the most reliable and effective method for diagnosing diseases that occur in the musculoskeletal system. The principle of manipulation is a different absorption of X-rays by muscle tissues. Soft tissues allow X-rays to pass through, but hard tissues absorb. An X-ray allows you to diagnose both the disease itself and its consequences.
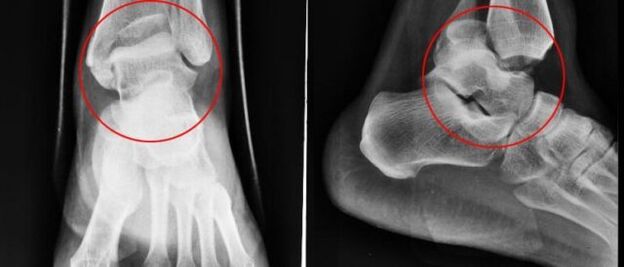
Conventional radiography is an examination method in which a small amount of x-rays are transmitted through a person's body or part of the body.
The snapshot allows you to see:
- The state of the bone surfaces in the joint.
- The shape, size and arrangement of the structures in the joint are relative to each other.
- The condition of the fabric.
- The size of the joint space.
These indicators help the doctor determine the type and extent of joint damage. If the data is not enough, doctors prescribe other studies.
With osteoarthritis of the ankle, an X-ray is performed in three projections:
- side;
- back;
- backward with one foot moved inward.
The disease is characterized by the following changes:
- joint space reduction;
- the presence of osteophytes;
- bone cartilage replacement (subchondral sclerosis);
- minor gaps in the periarticular part.
Nuclear magnetic resonance
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a diagnostic method allows you to study those parts of the body where there is water. The image shows bones in dark color, because they contain less water, but muscle tissue, discs, and nerves are lighter. MRI allows you to detect the slightest changes in the structure of bone tissue and joints. The study is also prescribed to patients before joint prostheses. YMG has a downside: a high price.
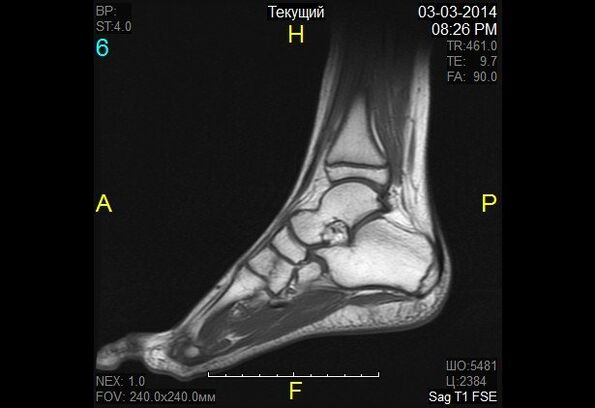
In nuclear magnetic resonance, a change in the properties of hydrogen molecules is recorded under the influence of a strong magnetic field.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an alternative diagnostic method that allows you to carefully examine the ligamentous structure of the joint, muscle, and cartilage tissue. With the help of an MRI, the doctor assesses the condition of the joints in the lower leg. According to the survey data, the pathology is revealed at an early stage of development.
The diagnostic principle is based on exposure to radio waves and strong magnetic radiation. The magnetic field used is not dangerous and does not pose a health risk.
Magnetic resonance imaging is contraindicated in cases of mental disorders, during pregnancy and in the presence of metallic objects in the human body.
When diagnosing osteoarthritis of the ankle, classic MRI machines (closed type) are used, as they have a better image quality. An MRI machine is a large cylindrical tube with a magnet around it. The patient lies on a special table. The ankle is fixed with a special coil. The procedure takes between 30 and 40 minutes. The study is absolutely painless. Patients may feel warm in the lower leg area.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination has been widely used in medicine since the 1990s of the 20th century. This technique has proven its worth in making accurate diagnoses. An ultrasound is also done for osteoarthritis of the ankle joint.
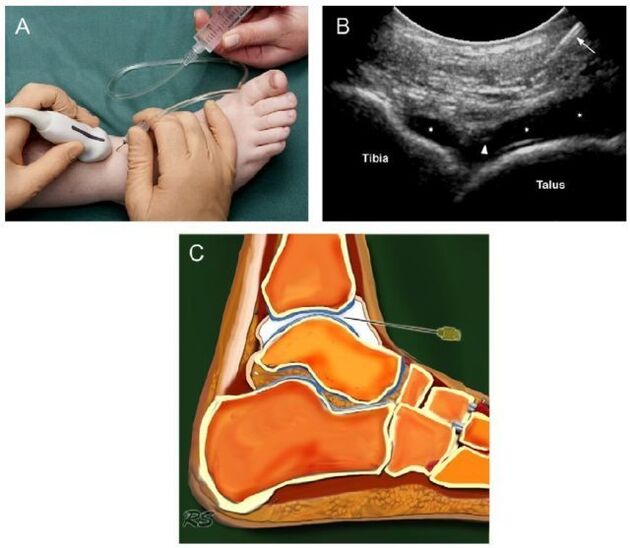
Today, ultrasound examination is not of particular importance in the diagnosis of osteoarthritis, as it does not allow a good enough study of damaged joints.
The device with which the study is carried out produces ultra-frequency waves. The waves are reflected off the tissues and recorded on the monitor. Based on the resulting image, the doctor determines the type of pathology. To clarify the image on the monitor, a special gel is used. Eliminates air gaps and gives the sensor better glide.
The ultrasound examination does not harm the patient, so the procedure can be repeated many times. The advantages of ultrasound also include low cost and high precision.
The following indicators are a clear sign of osteoarthritis:
- cartilage thinning;
- the presence of bone growths;
- accumulation of effusion in the joint cavity (synovitis);
- loss of cartilage space.
Bone scintigraphy
Scintigraphy is a high-precision study that, using isotopes, is capable of detecting pathological changes in the bones. Doctors divide pathogens into "cold" and "hot". In the first case, we are talking about areas in which there are no isotopes. These areas are poorly supplied with blood and are not visible during the examination. The "cold" areas are places that are affected by malignant tumors. In "hot" areas, isotopes accumulate quickly and look very bright when scanned. Such areas indicate the presence of inflammatory processes.
The role of scintigraphy in osteoarthritis is significant. The study helps distinguish osteoarthritis from other diseases when the clinical symptoms are extremely similar.
During a bone scan, a special preparation containing special labeled atoms is injected into the body.
Based on the results of the scan, the doctor makes a clinical prognosis and determines the treatment regimen. The only drawback of the study is its high cost. Scintigraphy is done with special equipment, and unfortunately not all medical institutions can afford to buy it.
Although radioactive scanning is a safe procedure, it still has a number of contraindications:
- the pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- taking medicines that contain barium.
When a radioactive substance is injected, some patients experience an allergic reaction in the form of itching and a rash. These side effects are not dangerous and go away on their own in a short time.
Joint puncture
Joint puncture is a diagnostic procedure in which a needle is inserted into the joint cavity to collect synovial fluid. This liquid is then sent for further investigation. Based on the data obtained, the doctor comes to a conclusion about the nature of the disease and the stage of its development.
At first glance, a puncture is a simple procedure, but it is not. Removal of fluid from the joint capsule requires exceptional precision of the physician's movements. The synovium is very thin and awkward movement traumatizes it. As a result, an inflammatory process develops. Potential risks also include infection. It is not difficult to carry the infection to the joint capsule through poorly sterilized instruments.
The manipulation technique is different for each joint. When collecting joint exudate from the ankle, the puncture is performed anteriorly, between the external ankle and the extensor digitorum longus tendon.
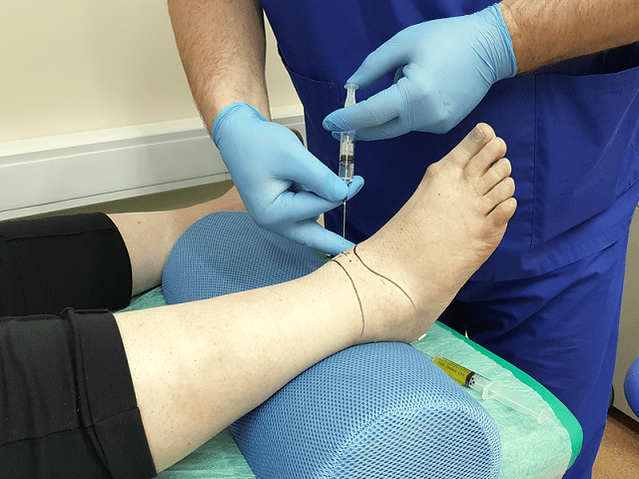
Diagnostic intra-articular fluid sampling allows laboratory analysis and excludes inflammatory arthritis.
Basic principles of treatment.
After confirming the diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the ankle joint, symptoms will soon appear. Treatment starts immediately. The additional prognosis depends on a well-chosen treatment regimen and the timeliness of initiation.
Osteoarthritis is an insidious disease. It cannot be completely cured. The goal of therapy is to stop degenerative processes and prolong the period of remission. For this, doctors prescribe drugs, physiotherapy, massages, recovery gymnastics and folk remedies. If all the conditions are met, it is possible to have positive dynamics, otherwise the disease progresses.
Pharmacological treatment for osteoarthritis.
Depending on the therapeutic effect, drugs are divided into several groups:
- Analgesics or anti-inflammatories. This group of drugs is aimed at eliminating the focus of inflammation and relieving pain. The earlier anti-inflammatory therapy is started, the better the chances of saving the joint. Drugs in this group can be produced in the form of tablets and ointments.
- Glucocorticoids. These drugs are prescribed when previous funds are ineffective. They are produced in the form of an injectable solution. The drug is injected directly into the joint.
- Chondroprotectors. Designed to slow down the destruction of cartilage.
The doctor selects the treatment regimen and dose, based on the severity of the symptoms, the age of the patient, the presence of comorbidities, and other factors. Self-medication is dangerous and often aggravates the situation, as many of the drugs have various side effects and their own contraindications.

Characteristics of radical treatment.
If conservative therapy has failed, doctors are forced to resort to a radical treatment method (surgical intervention). The operation is also displayed when:
- secondary (post-traumatic) and primary osteoarthritis of 3-4 degrees;
- osteoarthritis with complications;
- constant and severe pain in the ankle, radiating to the knee;
- severe lameness;
- paresis and paralysis of the leg muscles;
- violation of the flexion-extension function of the joint;
- violation of the supporting ability of the foot.
Surgical intervention is contraindicated if:
- the patient is less than 12 years old;
- fistulas are found in the joint;
- the patient has a history of diabetes mellitus, heart failure;
- Infectious diseases were found in the area of the proposed intervention.
Traditional treatment
Doctors believe that the treatment of arthrosis should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of a specialist, but they do not deny the positive effect of folk remedies. Alternative medicine acts as an effective prophylaxis that helps eliminate symptoms and maintain remission.

Home remedies are a fairly symptomatic treatment for osteoarthritis of the foot.
Home treatment should be coordinated with your doctor to avoid side effects and complications.
Traditional healers suggest treating ankle osteoarthritis with:
- Burdock. Wash the burdock leaves under running water and soap. Apply the leaves with the smooth side to your skin. Fix the upper part with a bandage or cling film. It is better to keep the compress overnight.
- Sea salt. Chop the salt in a skillet. Pour it into a linen bag and place it on your ankle. Hold the bag until the salt has cooled. Heat relieves pain. Sand, lentils, buckwheat are also used instead of salt.
- Lilacs Pour the triple colony over the lilac flowers. Let the tincture stand in a cool, dark place for 10-14 days. Rub the affected area in the morning and at night.
- Eggshell. Grind the shells in a coffee grinder. Take the resulting powder for ½ teaspoon. before eating.
Do not forget that treatment with folk remedies should not be the only measure. Complex treatment includes taking medication, exercise therapy, massage, physical therapy, spa treatments. In advanced cases, doctors resort to radical measures - surgical intervention.
Surgery
For osteoarthritis of the foot, the following types of operations are used in medicine:
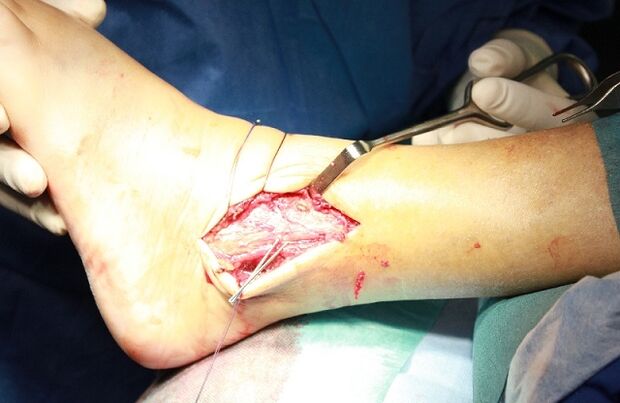
- arthrodesis of the joint;
- joint arthroscopy;
- endoprosthesis.
Arthrodesis is an operation to immobilize a joint. It is carried out to return the limb of lost support capacity. The only downside to the surgery is that the bones (tibia and talus) grow together, which leads to immobility. Arthrodesis is rarely used in medical practice.
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure. During the operation, the doctor makes small incisions in the joint area and through them inserts an arthroscope (a special tube at the end of which a camera is installed). With the help of him, the surgeon carefully examines and assesses the condition of the intra-articular structures. If necessary, pieces of the damaged joint or blood clots are removed from the synovial fluid. This manipulation is less traumatic. The only downside to arthroscopy is that the risk of recurrence is too high.
The endoprosthesis is a treatment of last resort. It is performed with advanced osteoarthritis. The endoprosthesis allows you to replace the affected joint partially or completely. As a prosthetic product, innovative prostheses with modernized mechanics are used. An artificial joint lasts 10 to 20 years.
Power functions
To achieve a favorable result, drug treatment is supplemented with dietary therapy. Nutritionists have developed a special diet to prevent exacerbation of the disease and at the same time provide the body with all the necessary vitamins and nutrients. The diet for overweight patients plays a special role. Since obesity is one of the reasons for the development of osteoarthritis, weight correction is an integral part of treatment.

The patient must reconsider some of his habits in daily life, which contribute to and cause the progression of osteoarthritis of the foot.
Nutritionists recommend adhering to the following nutritional conditions:
- Eat often and in small portions.
- Drink at least 2 liters of liquid a day.
- Give up sweets and salt.
- The last meal is at the latest at 6: 00 p. m.
- Dishes can be steamed, boiled or baked.
The main task of the diet for osteoarthritis is balanced and enriched nutrition. Fasting is out of the question. Harsh diets and body cleansing do more harm than good. Calcium is removed from the body, which is necessary for cartilage restoration. A nutritionist will help you compose a daily diet.
With osteoarthritis, it is allowed to eat cereals, pasta, dairy products, cheese, legumes, vegetables, fruits, rye bread, dried fruits, nuts, fish, poultry. Heavy and greasy side dishes, foods containing colors and flavors, as well as pickles, marinades, smoked meats, fatty broths, baked goods, spices, sauces, chocolate, ice cream, coffee and alcohol are prohibited.
Prevention of osteoarthritis
To avoid the development of arthrosis of the ankle joint, doctors recommend taking preventive measures:
- wear comfortable shoes without heels;
- follow a diet and drink enough fluids;
- seasonally take vitamin-mineral complexes;
- swimming;
- walk more outdoors;
- eliminate excessive stress on the legs;
- avoid hypothermia;
- be examined by a doctor in a timely manner.
With existing arthrosis, it is recommended to correct the lifestyle:
- Reject bad habits. They have been shown to cause stagnation of blood in tissues and accelerate the destruction of cartilage.
- Do a series of exercises to warm up your ankle.
Forecast
Osteoarthritis is a progressive disease. Without treatment, it leads to irreversible consequences and complete immobility of the joint. Early diagnosis of pathology allows you to do without radical measures. Medications can suspend the disease process and alleviate the patient's condition. Fighting the disease in the early stages is uncomplicated.



































